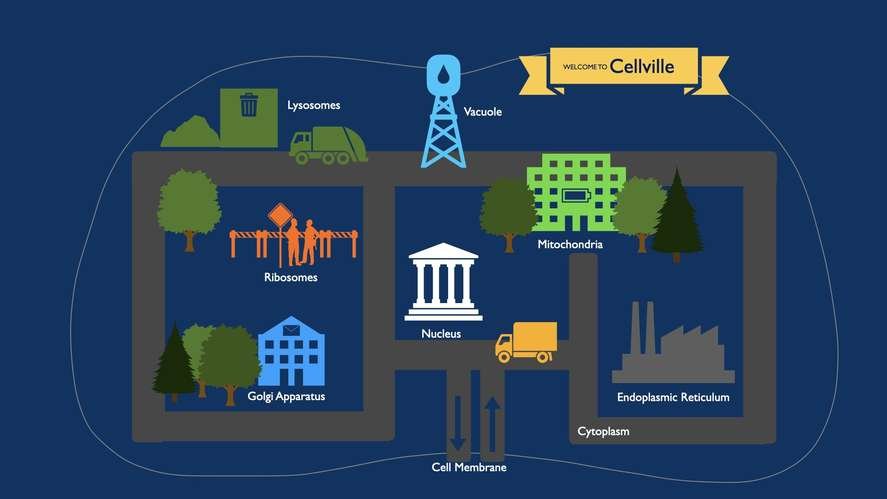
Cell City is a fascinating concept that simplifies the complexities of a cell by comparing it to a bustling metropolis. In this miniature urban landscape, each organelle plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell’s function and survival. From the powerhouse of mitochondria to the transportation network of the endoplasmic reticulum, Cell City showcases the dynamic interactions within a cell. Let’s embark on a virtual tour of this microscopic city to uncover the hidden marvels of cellular architecture. Step into Cell City and witness the vibrant community thriving within each living cell. Welcome to the cellular metropolis!
Exploring the Fascinating World of Cell City: A Fun and Educational Adventure
Welcome, young scientists, to the marvelous world of Cell City! Today, we are going on an exciting journey to uncover the secrets of the smallest metropolis in nature – the cell. Just like a bustling city filled with different buildings and neighborhoods, a cell is a bustling community of organelles and structures working together to keep living organisms alive and functioning. So put on your lab coats and let’s dive into the amazing world of Cell City!
The Basics of Cell City
Imagine a city where every part has a specific role to play, just like the different organelles in a cell. At the very core of Cell City lies the nucleus, which acts as the control center, directing all the activities within the cell. It’s like the mayor of the city, making sure everything runs smoothly.
Surrounding the nucleus are the streets and highways of Cell City, known as the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. These structures are like the transportation system of the cell, helping to move materials around quickly and efficiently.
But what about the power source of Cell City? That’s where the mitochondria come in. These energy-producing organelles are like the power plants of the city, providing the energy needed for all cellular activities.
Exploring the Neighborhoods: Different Organelles of Cell City
The Nucleus: The City’s Command Center
Let’s start our exploration of Cell City with the nucleus, the most important organelle in the cell. Just like a city’s command center, the nucleus contains the cell’s DNA, which carries all the instructions needed for the cell to function properly.
Think of the DNA as the city’s blueprint, containing all the information about how Cell City should be built and what each part should do. The nucleus carefully protects and manages this valuable information, ensuring that the city operates smoothly.
The Mitochondria: Power Plants of Cell City
Now, let’s hop over to the mitochondria, the power plants of Cell City. These tiny organelles are responsible for generating energy through a process called cellular respiration. Just like a power plant converts fuel into electricity for a city, mitochondria convert nutrients into energy that the cell can use to carry out its various functions.
Without the mitochondria, Cell City would quickly run out of energy and come to a standstill. These powerhouse organelles work tirelessly to keep the city up and running, providing the fuel needed for all cellular activities.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Apparatus: The Transportation System
As we navigate through Cell City, we encounter the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, the transportation system that ensures materials are moved from one part of the cell to another with precision and efficiency.
Just like trucks and trains transport goods through a city, the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus package and transport proteins and other molecules to their designated locations within the cell. Without this organized transportation system, Cell City would be in chaos, with important materials getting lost or misplaced.
Specialized Buildings: Different Cell Types in Cell City
While all cells share common organelles and structures, different cell types in Cell City have specialized buildings that allow them to perform specific functions. Just like in a real city where different neighborhoods serve different purposes, specialized cells have unique features that enable them to carry out specific tasks.
Neuron: The Communication Center
Imagine a bustling office building in the heart of Cell City known as the neuron. This specialized cell type acts as the communication center, transmitting electrical signals to different parts of the body. Just like a telephone exchange in a city, neurons play a crucial role in coordinating responses to stimuli and allowing us to think, move, and feel.
Muscle Cell: The Powerhouse
In another part of Cell City, we find the muscle cell, a powerful building responsible for movement and strength. Just like a gym in a city where people go to exercise and build muscles, muscle cells are packed with specialized proteins that enable them to contract and generate force. Without muscle cells, we wouldn’t be able to move, run, or jump!
Red Blood Cell: The Oxygen Couriers
As we explore further, we come across the red blood cell, essential couriers that transport oxygen throughout the body. These specialized cells are like delivery trucks, carrying oxygen from the lungs to every part of Cell City to keep the residents alive and energized. Without red blood cells, the city would quickly suffocate and cease to function.
Keeping Cell City Healthy: Maintaining Balance and Harmony
Just like a real city requires maintenance and upkeep to stay functional, Cell City also needs to maintain balance and harmony to ensure the well-being of its residents. This involves processes like cell division, waste disposal, and responding to environmental changes.
Cell Division: Building New Homes
One of the key processes that keep Cell City thriving is cell division, where cells replicate and create new homes for residents. Just like constructing new buildings in a city to accommodate a growing population, cell division ensures that Cell City can grow, repair damaged parts, and replace old or dying cells.
Waste Disposal: Keeping the City Clean
Every city needs a waste disposal system to keep the streets clean and free of clutter. In Cell City, organelles like lysosomes act as garbage disposals, breaking down and recycling cellular waste products. Without these cleaning crews, Cell City would quickly become overwhelmed with trash and debris, hindering its functions.
Responding to Environmental Changes: Adapting to Challenges
Just like how a city must adapt to changing weather conditions or natural disasters, cells in Cell City must respond to environmental changes to survive and thrive. Cells have intricate signaling pathways that enable them to detect and respond to external cues, ensuring that the city remains resilient and can overcome challenges.
Conclusion: Celebrating the Marvels of Cell City
As we conclude our exploration of Cell City, we have uncovered the intricate and fascinating world that exists within the smallest units of life. From the bustling organelles to the specialized cell types, Cell City is a vibrant and dynamic community where every part plays a crucial role in maintaining life.
So next time you look at a cell under a microscope, remember that you are peering into a miniature city teeming with activity and complexity. Just like a city thrives when its residents work together in harmony, cells in Cell City rely on teamwork and cooperation to function effectively and keep living organisms healthy and alive.
Thank you for joining me on this educational adventure through Cell City. Stay curious, keep exploring, and remember – the wonders of science are just waiting to be discovered!
Cell City
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the structure of a cell city?
In the analogy of a cell city, a cell’s structure is compared to various components of a city. The cell membrane acts as the city limits, controlling what enters and exits. The nucleus serves as the city hall, regulating activities within the city. Organelles are like different buildings, each with specific functions, such as the mitochondria acting as power plants and the Golgi apparatus as the post office.
How do cells communicate within the “cell city”?
Cells communicate within the “cell city” through various methods. Just like citizens in a city talk to each other, cells use signaling molecules to send messages. These molecules travel through the cell membrane and interact with receptors on other cells to initiate responses. This communication is crucial for coordinating activities within the cell city and maintaining homeostasis.
What is the role of mitochondria in the cell city analogy?
In the cell city analogy, mitochondria are often referred to as the power plants. Just like power plants generate energy for a city, mitochondria produce energy in the form of ATP for the cell. This energy is essential for various cellular activities, including growth, repair, and movement. Without functioning mitochondria, the cell city would lack the energy needed to sustain its operations.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the intricate structures of a cell city mirror that of a bustling metropolis. Each organelle plays a vital role in maintaining cellular functions, akin to different departments in a city. Just as a city thrives when all sectors work in harmony, a cell city functions efficiently through well-coordinated organelles. Understanding the dynamics of a cell city offers valuable insights into the complexities of life at a microscopic level.